Recurrent Neural Network (Professor 李宏毅 ML #26 0-45 mins)
Chien-Chang Chen 03/09/2018
With the following online source [0],
this document introduces the role of recurrent neural network (RNN) in speech recognition.
Mechanism of RNN
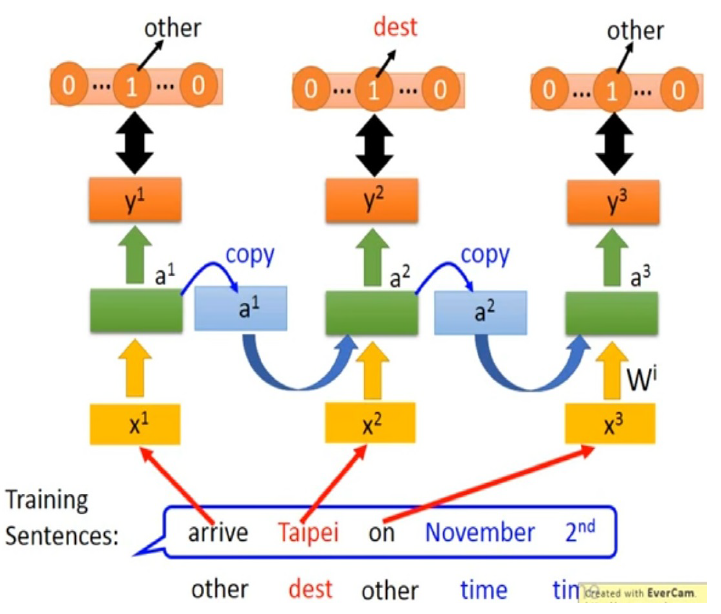 Schematic of RNN-based slot fitting.
Schematic of RNN-based slot fitting.
Fig. shows an exemplary schematic of RNN-based slot fitting.
The RNN, depicted by green box, has an input sequence , and an output slot sequence .Our goal is to fit the input sequence `arrive at Taipei on November 2nd'' to the slot sequence`other dest other time time''.
In the -th step, and the -th loss function , are calculated, and the -th weight are chosen to minimize . can be defined as the sum of cross entropy between the output and a reference parameter , ; is an identity vector, where the non-zero entry is the slot belongs to.
can be obtained by applying gradient descent method, namely,
where is the learning rate at the -th step. A algorithm called backpropagation through time (BPTT) can be used for the implementation of gradient descent in RNN.
Gradient Vanishing Problem in RNN
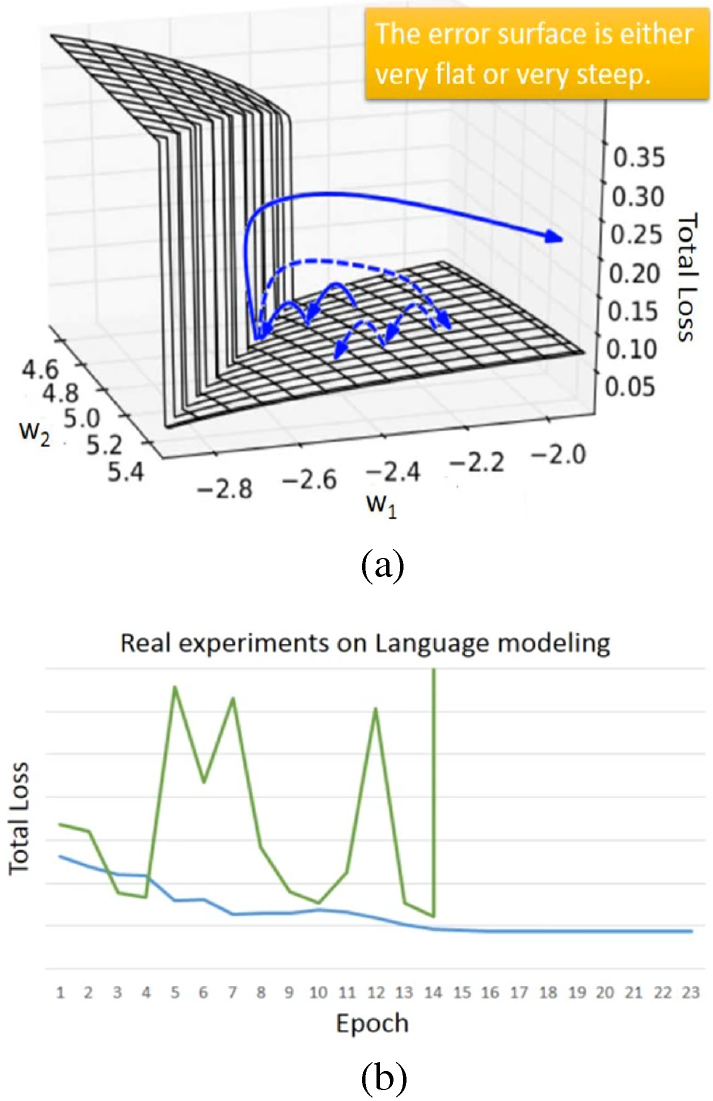
(a) Error surface in regards to and (b) the total loss-epoch diagram.
Fig. (a) shows an exemplary error surface of RNN in regards tos to and ,Long short-term memory (LSTM), gated recurrent unit (GRU), clockwise RNN and structurally constrained recurrent network (SCRN)
can handle gradient vanishing problem. Hence, larger learning rate can be set.
Since GRU require lesser parameters than LSTM, the former is more robust than the latter.
steeply ascends at , and the updated may be forced out of the domain,
which is gradient explode.
Clipping, in which are bounded by a specified constant value, can handle gradient explode problem.
Fig. (b) shows the exemplary total loss-epoch diagram, where gradient explode occurs
and lead to the divergence of total loss.
The Application of RNN
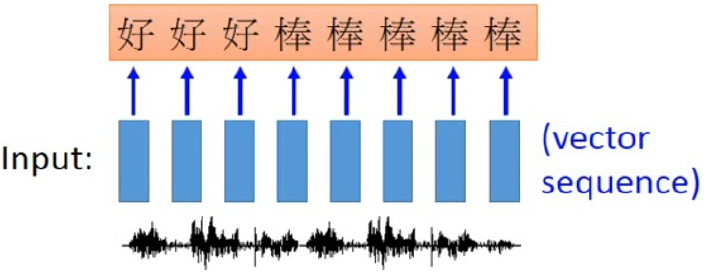
Application of RNN in speech recognition.
Fig shows an application of RNN in speech recognition,
where the length of output sequence is shorter than that of input.
The input speech vector sequence, depicted by blue boxes, are trained by RNN to output character sequence.
Since the speech signal are extracted every several millisecond, e.g. 0.01 second,
the first three speech vectors map to character `hao'; while the last five speech vectors map to character `bun'.
The output character sequence then undergo a trimming process to eliminate repeated character.
As a result, we get ``hao bun''.
However, the word sequence ``hao bun bun'', containing reduplication, will not be able to recognized correctly.
Connectionist temporal classification (CTC), which allows the recognition of NULL symbol, can handle reduplication in Chinese.
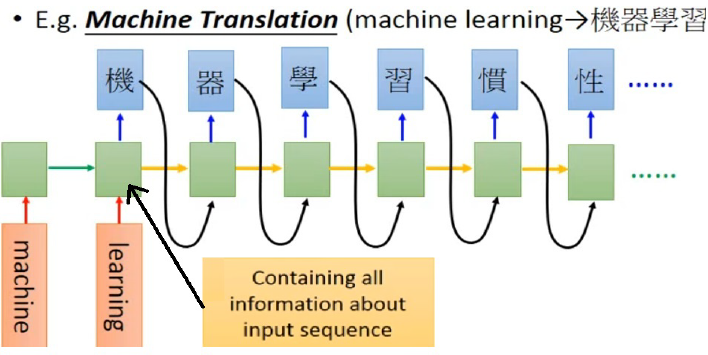
Application of RNN in translation.
Fig shows an application of RNN in translation,
where the length of output sequence is unsure.
The input English word sequence ``machine learning'' in has to be tranalate to Chinese word sequence ``Gi Chi Shua Shi''.
After reading ``machine learning'', all information about input sequence are contained in RNN,
then it starts to correctly output Chinese word "Gi Chi Shua Shi" accordingly.
However, since the length of output is unsure, RNN will not stop.
This issue can be handled with the incorporation of a halt symbol in the output that tells RNN to stop.
[0]
H. Y. Lee, ML lecture #26, RNN part II
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rTqmWlnwz_0