Recurrent Neural Network (Professor 李宏毅 ML #26 45-90 mins)
Ben 03/13/2018
RNN的機制
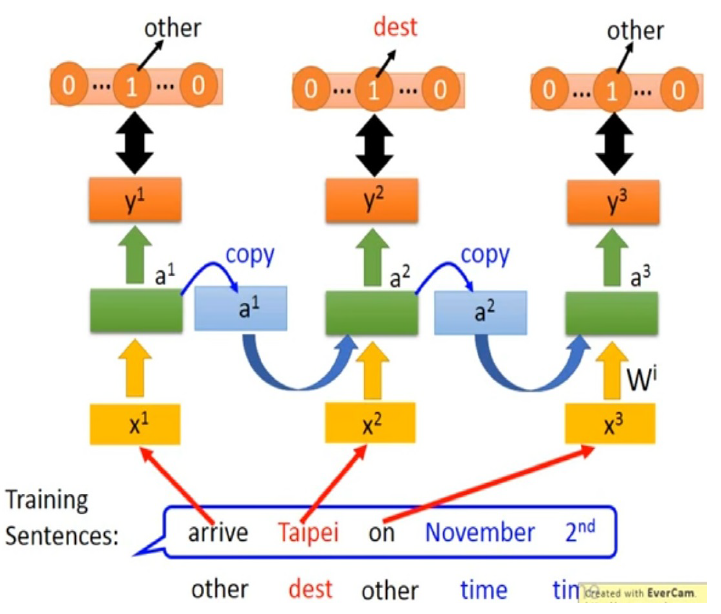
圖一. 使用RNN預測字詞,訓練過程運作示意圖.
圖一 呈現使用RNN預測字詞的訓練過程示意圖。
綠色方框是RNN模型, 是RNN的輸入字詞,是RNN的輸出類別。
當第一個字詞arrive輸入時,我們希望RNN的輸出是other的機率最大;
當第二個字詞Taipei輸入時,我們希望RNN的輸出是dest (destination)的機率最大;
當第三個字詞on輸入時,我們希望RNN的輸出是other的機率最大;
當第四個字詞November輸入時,我們希望RNN的輸出是time的機率最大;
當第四個字詞輸入時,我們希望RNN的輸出是time的機率最大;
定義
其中,。
可以由gradient descent method計算為
其中 是學習效率係數 (learning rate),上標n表是他也可以隨著跌代而不同數值。
backpropagation through time (BPTT)技術被用來執行RNN的gradient descent 計算。
RNN的梯度消失議題
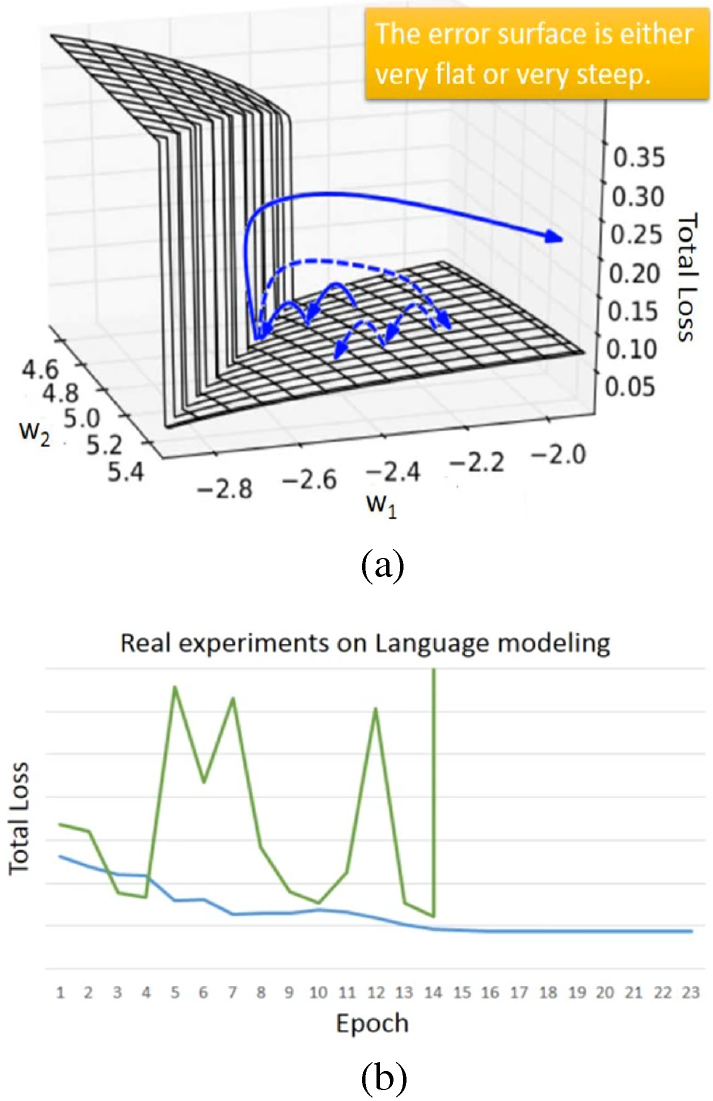
(a) Error surface in regards to and (b) the total loss-epoch diagram.
Fig. (a) shows an exemplary error surface of RNN in regards tos to and ,Long short-term memory (LSTM), gated recurrent unit (GRU), clockwise RNN and structurally constrained recurrent network (SCRN)
can handle gradient vanishing problem. Hence, larger learning rate can be set.
Since GRU require lesser parameters than LSTM, the former is more robust than the latter.
steeply ascends at , and the updated may be forced out of the domain,
which is gradient explode.
Clipping, in which are bounded by a specified constant value, can handle gradient explode problem.
Fig. (b) shows the exemplary total loss-epoch diagram, where gradient explode occurs
and lead to the divergence of total loss.
The Application of RNN
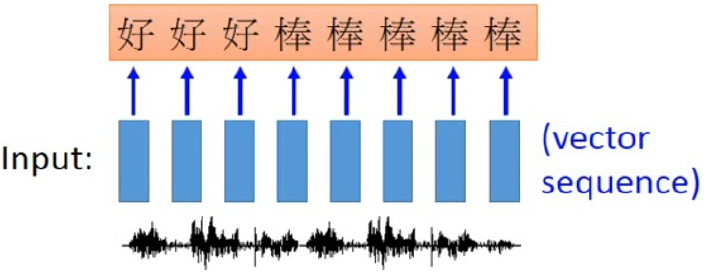
Application of RNN in speech recognition.
Fig shows an application of RNN in speech recognition,
where the length of output sequence is shorter than that of input.
The input speech vector sequence, depicted by blue boxes, are trained by RNN to output character sequence.
Since the speech signal are extracted every several millisecond, e.g. 0.01 second,
the first three speech vectors map to character `hao'; while the last five speech vectors map to character `bun'.
The output character sequence then undergo a trimming process to eliminate repeated character.
As a result, we get ``hao bun''.
However, the word sequence ``hao bun bun'', containing reduplication, will not be able to recognized correctly.
Connectionist temporal classification (CTC), which allows the recognition of NULL symbol, can handle reduplication in Chinese.
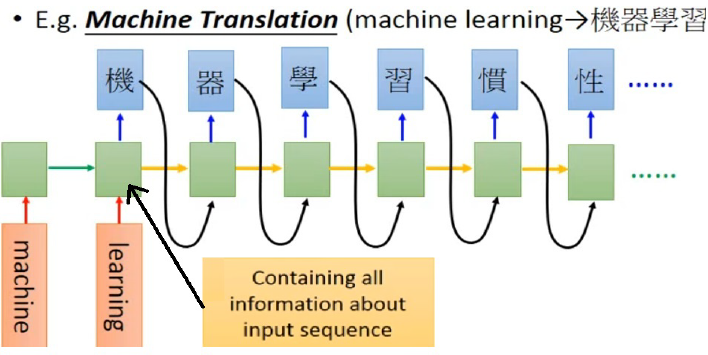
Application of RNN in translation.
Fig shows an application of RNN in translation,
where the length of output sequence is unsure.
The input English word sequence ``machine learning'' in has to be tranalate to Chinese word sequence ``Gi Chi Shua Shi''.
After reading ``machine learning'', all information about input sequence are contained in RNN,
then it starts to correctly output Chinese word "Gi Chi Shua Shi" accordingly.
However, since the length of output is unsure, RNN will not stop.
This issue can be handled with the incorporation of a halt symbol in the output that tells RNN to stop.
learning需要有cost function (也稱做loss function)。cost function就是計算cross entropy。
(每個時間點的cross entropy)。 有了loss function後,便將loss function對w (weight,RNN的權重參數)微分,。
而網路的權重調整為:
BPTT的演算法來計算這些微分運算。
訓練的過程,Loss應該慢慢地會下降,而RNN不容易訓練,loss很容易沒有收斂。 過去以為是有程式bug。 後來發現其實是RNN的error surface很不平滑。 就像是懸涯峭壁,懸崖上的的gradient很大, 若是踩在懸崖上,調整參數(w)之後就飛出去了。
發明word vector的人有很長一段時間只有他能train起model
最後他在他的博士論文解到解決懸崖上gradient很大的方法是:Clipping,如果gradient value> specific value,就設定為specific value
Sigmoid function可以讓gradient非常的小嗎?
ReLU
改變w的時候,對於最後的output的影響會有多大呢?
Gradient>1設定small learning rate
Gradient<1設定large learning rate
這樣會造成我們很難調整learning rate
難training RNN的原因不是在activation,而是在gradient
Solution: Long Short-term Memory
可以解決gradient vanishing的問題
RNN和LSTM在面對memory裡面的資訊,operation是不一樣的
RNN每次memory都會被完全洗掉
LSTM把原來memory*值+ input放入cell裡面
OH~ LSTM裡面會對memory影響的值只要一產生之後,就會一值存在
LSTM 1997年提出,當初沒有forget gate,總共有3個gate
用gate操控memory的cell: gated recurrent unit(GRU)只有兩個gate
精神是:舊的不去,新的不來
forget gate
input gate之間的關係
identity
many vectors to one vector
利用RNN給machine去看一篇文章,他會去找裡面有哪些關鍵詞彙?
Many vector to many vectors
長sequence轉成短sequence
e.g. speech recognition
為了要把好棒跟好棒棒分開
那就用了一招connectionist temporal classification(CTC)
多了一個null值
因此,CTC Training
窮舉所有的alignments當成都是正確的
有個巧妙的演算法解決不用全部列完的
英文辨識英文字母+空白
傳說google的語音辨識,現在已經全部都轉換成CTC training了
如果沒有出現過的詞彙第一次被講,也能被正確的辨識出來
不知道英文和中文裡,input & output哪個長?哪個短?
推文接龍
回到machine learning裡面,add a symbol ===讓他斷掉
Google brain:seq 2 seq learning
Input某種語言的聲音 opunt另種語言的文字
英文的聲音訊號轉成中文的文字
目前有做到輸入法文語音,model已經可以做到可辨識成中文
需要有語音和對應的翻譯丟進去
做到beyond sequence
產生syntactic parsing如何讓machine得到一個樹狀結構?
有了seq 2 seq之後,
過去要用structure learning的技術,只需要把樹狀圖描述成一個sequence
Output就是一個syntactic parsing tree,就可training起來
考慮Word sequence的情況之後,來解決字彙量一樣,但組起來語句不同的問題=> seq 2 seq encoder接著可以具有hierarchy
同時也可以用到speech上,
語音的搜尋
不需要聲音辨識,只需要做聲音相似度的辨識即可audio segment to vector
Audio segment => acoustic features => RNN encoder => RNN Decoder
LSTM encoder => LSTM decoder
除了RNN以外,有用到memory的model是attention-based model
Input => DNN/RNN => ouput
多了reading head controller及writing head controller
稱為Neural Turing Machine
Query=>中央處理器(DNN/RNN)去控制reading head controller如果讀到相關的information之後,就把header放在上面,再放回去DNN/RNN=> get answer
Keras有example在處理讀一句話回答答案
可以餵機器visual /語音輸入(TOFEL),來回答答案
實驗結果隨意猜的結果是25%
shortest或是一選項和另外三個選項語意相關的話,這兩種方法可以到達35%
Memory Network可以達到39.2%
proposed approach:可以到達48.8%
Deep & Structure Learning的關係
| RNN, LSTM | HMM, CRF, Structured Perceptron/SVM |
|---|---|
| Unidirectional RNN不考慮整個seq | 因為用Viterbi,所以可考慮整個seq |
| Cost和error往往沒有關係 | 可以很explicitly去考慮label間關係?可以 |
| 可以是deep | Cost function是error的上界 |
| Deep Leaning可以佔到比較大的優勢 |
Input feature先通過RNN/LSTM,再餵到HMM, CRF, Structured Perceptron/SVM
語音辨認: CNN/LSTM/DNN +HMM
RNN是一個一個frame去看
語意tagging: Bi-directional LSTM+ CRF/Structured SVM
Structure learning要解三個問題
1.Inference
2.解inference的問題,要窮舉所有的可能
3.How to learn how to learn F(x)
把GAN中的discriminator看成evaluation function可以解Problem 1
把generator當成可以窮舉所有的可能
Conditional GAN
Discriminator會去Check real (x,y) pair
Input x => image y => discriminator就會去檢查畫和圖是不是一樣?
learning需要有cost function (也稱做loss function)。cost function就是計算entropy。是每個時間點的cross entropy。有了loss function後,便將loss function對w (weight,RNN的權重參數)微分。BPTT的演算法來計算這些微分運算。RNN不容易訓練,loss很容易沒有收斂。過去以為是有程式bug。後來發現其實是RNN的error surface很不平滑。就像是懸涯峭壁,懸崖上的的gradient很大,若是踩在懸崖上,調整參數(w)之後就飛出去了。
Recurrent neural network training data就是訓練RNN的資料。(這邊再聽一次便再補進文章)
[0]
H. Y. Lee, ML lecture #26, RNN part II, at